Answer
Calculus 8th Edition answers to Chapter 2 - Derivatives - 2.1 Derivatives and Rates of Change - 2.1 Exercises - Page 113 1 including work step by step written by community members like you. Textbook Authors: Stewart, James, ISBN-10:, ISBN-13: 978-1-28574-062-1, Publisher: Cengage. The average rate of change is (y2-y1)/(x2-x1). It is the same as the slope.) In this question, x1 = -1, so y1 = 2 ans x2 = 3, so y2=10. Chapter 2 Thomas Calculus solution 11th 12th 13th 14th edition solution manual Urdu Hindi The topics of discussion are Average rate of change of functions. Unit 1 – Limits and Continuity; Unit 2 – Differentiation: Definition and Fundamental Properties. 2.1 Defining Average and Instantaneous Rates. Thus the average energy of the reaction is (e 2 + 1)/ 4(e – 1) , or roughly 1.22. Mean Value Theorem for Integrals. Averages are also called means. So you may use the same formula to find the mean value of a function. There is also an important result in calculus that relates the mean value to a particular function value on the given interval.
Work Step by Step
2.1 Average Rate Of Changeap Calculus Equation
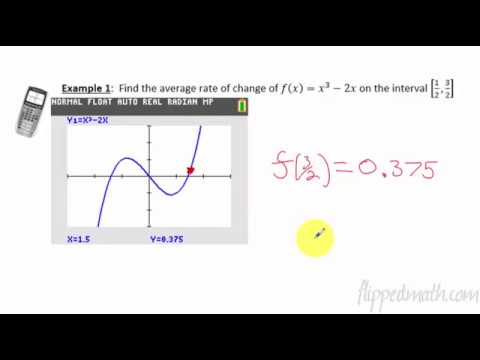
2.1 Average Rate Of Changeap Calculus Formula
